ENCQOR 5G has now helped over 450 small and medium enterprises in Canada gain access to pre-commercial 5G technology. This proves that many companies see an opportunity with 5G either to define new products and services or that 5G will enable the digitalization of sectors and industries that have yet to transform. If you still have some doubts, hopefully this newsletter will provide some additional arguments taken from some very methodological market studies and interviews that Ericsson conducts regularly across the globe.
Value of digital infrastructure
Changes in behavior due to lockdown restrictions have caused measurable changes in the usage of both fixed and mobile networks. The largest share of the traffic increase has been absorbed by fixed residential networks, which has experienced a 20-100 percent growth. But many service providers also noticed a spike in demand on their mobile network.
In a recent study conducted by Ericsson Consumer Lab, 83 percent of the respondents from 11 countries claim that ICT helped them a lot to cope with the Covid-19 lockdown. The results show an increased adoption and usage of ICT services, such as e-learning and wellness apps, that have helped consumers adapt to new realities, underpinned by connectivity.
Looking ahead, while 57 percent say they will save money for financial security, one-third plan to invest in 5G and an improved broadband at home to be better prepared for a potential second wave of COVID-19.
Ericsson expects the global number of 5G subscriptions to top 190 million by the end of 2020 and 2.8 billion by the end of 2025. These forecasts are included in the June 2020 edition of the Ericsson Mobility Report, along with projections for data traffic growth, and regional subscriptions. The report also takes an incisive look at the role of networks and digital infrastructure in keeping societies running, and families connected during the COVID-19 pandemic.
While 5G subscription growth in some markets has slowed as a result of the pandemic, this is outweighed by other markets where it is accelerating, prompting Ericsson to raise its year-end 2020 forecast for global 5G subscriptions. However, the success of 5G cannot be measured in subscriptions alone. The value 5G brings will be determined by the success of new use cases and applications for consumers and businesses. Many believe that 5G is the first wireless “G” or generation to specifically address industry requirements such as dealing with millions of connected devices deployed in small geographic areas or Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications. This will unlock scenarios and solve challenges that are simply not possible with existing networks.
The June 2020 edition of the Ericsson Mobility Report is filled with charts and graphs of very recent data that give insights on many facets of 5G. Its adoption, deployment and use cases. Below are just two examples of what you will find in the report.
Key Figures, Data and Forecasts
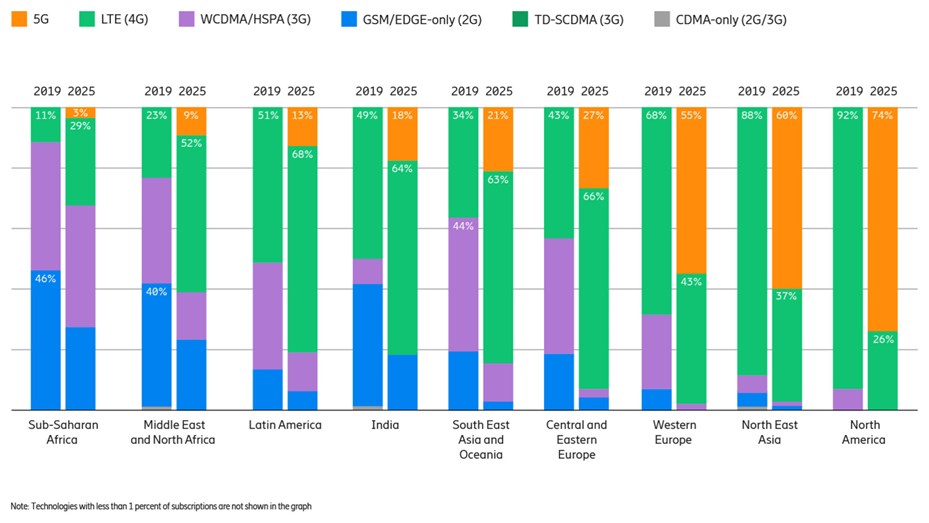
Regional subscriptions outlook
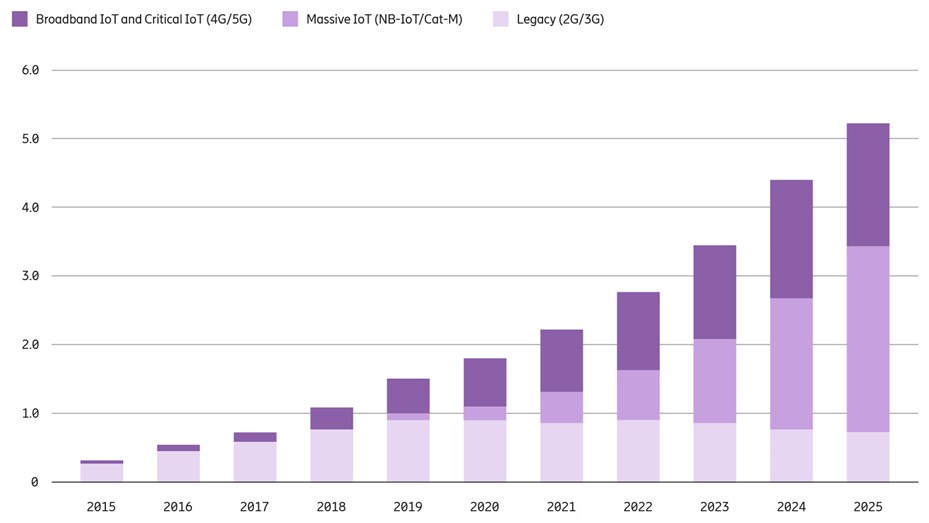
IoT connections outlook
Massive Internet of Things (IoT) primarily consists of wide-area use cases, connecting large numbers of low-complexity, low-cost devices that have long battery life and relatively low throughput. NB-IoT and Cat-M technologies complement each other; out of the 123 service providers [ GSA (April 2020)] identified as having launched at least one of these, 25 percent have launched both. At the end of 2025, NB-IoT and Cat-M are projected to account for 52 percent of all cellular IoT connections. Cat-M and NB-IoT follow a smooth evolution path into 5G networks and can continue to be deployed in the same bands as today, even when 5G is introduced. Commercial devices for Massive IoT include various types of meters, sensors, trackers and wearables. ENCQOR 5G’s platform supports both.
Broadband IoT mainly includes wide-area use cases that require higher throughput, lower latency and larger data volumes than Massive IoT technologies can support. LTE is already supporting many use cases in this segment. By the end of 2025, 34 percent of cellular IoT connections will be broadband IoT, with 4G connecting the majority. With the introduction of 5G New Radio (NR) in old and new spectrum, throughput data rates will increase substantially for this segment. ENCQOR’s 5G platform supports this.
Critical IoT is used for time-critical communications in both wide- and local-area use cases that require guaranteed data delivery with specified latency targets. Critical IoT will be introduced in 5G networks with the advanced time-critical communication capabilities of 5G NR. Deployment of the first modules supporting Critical IoT use cases is expected in 2021. Typical use cases include cloud-based AR/VR, cloud robotics, autonomous vehicles, advanced cloud gaming, and real-time coordination and control of machines and processes. Several of these use cases are supported by ENCQOR 5G’s platform.